What is Big Data? Characteristics and Types of Big Data
Recently the term ‘Big Data’ has been under the limelight, but not many people know what is big data.
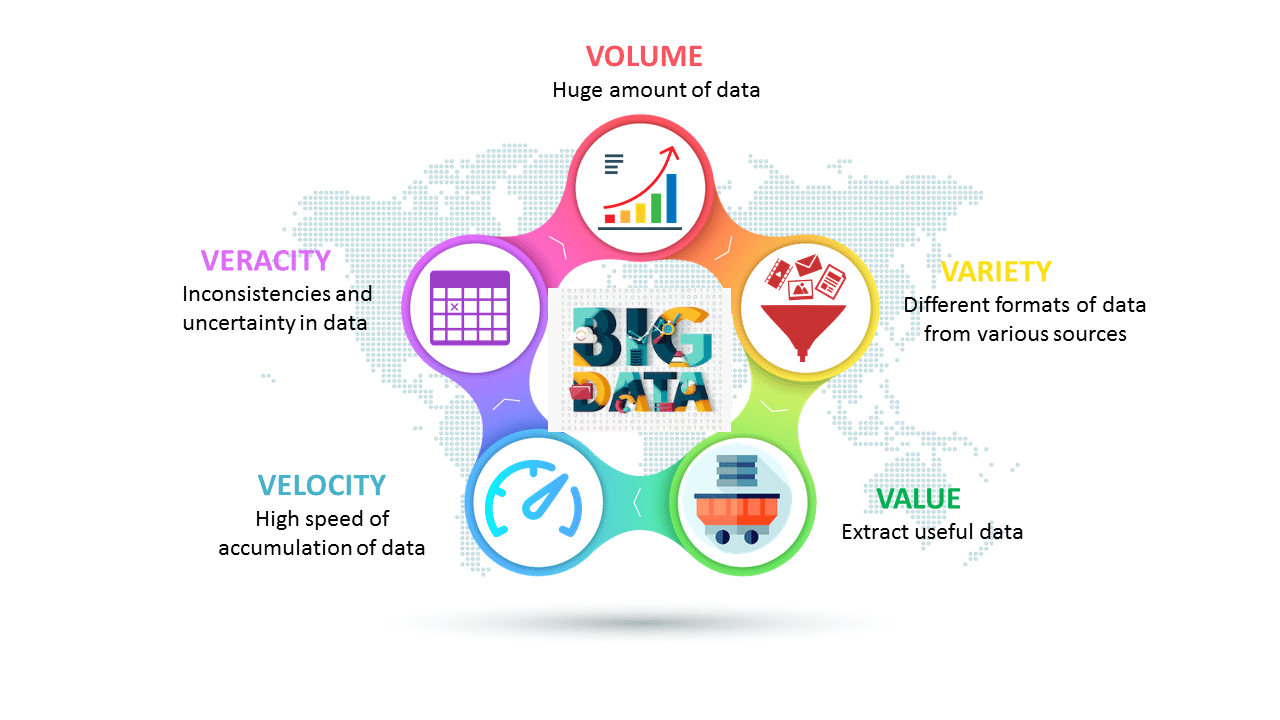
Here is Gartner’s definition, circa 2001 (which is still the go-to definition): Big data is data that contains greater variety arriving in increasing volumes and with ever-higher velocity. This is known as the three Vs.
Characteristics of Big Data / what is big data Characteristic:
Listed are the 3 ‘V’s of Big Data – Variety, Velocity, and Volume. Let’s discuss the characteristics of big data.
These characteristics, isolated, are enough to know what is big data. Let’s look at them in-depth:
Volume: Organizations collect data from a variety of sources, including business transactions, smart (IoT) devices, industrial equipment, videos, social media, and more. In the past, storing it would have been a problem – but cheaper storage on platforms like data lakes and Hadoop have eased the burden.
Velocity: With the growth in the Internet of Things, data streams into businesses at an unprecedented speed and must be handled in a timely manner. RFID tags, sensors, and smart meters are driving the need to deal with these torrents of data in near-real-time.
Variety: Data comes in all types of formats – from structured, numeric data in traditional databases to unstructured text documents, emails, videos, audios, stock ticker data, and financial transactions.
Types of Big Data
Now that we are on track with what is big data, let’s have a look at the types of big data:
Structured
Structured is one of the types of big data and By structured data, we mean data that can be processed, stored, and retrieved in a fixed format. It refers to highly organized information that can be readily and seamlessly stored and accessed from a database by simple search engine algorithms. For instance, the employee table in a company database will be structured as the employee details, their job positions, their salaries, etc., will be present in an organized manner.
Unstructured
Unstructured data refers to the data that lacks any specific form or structure whatsoever. This makes it very difficult and time-consuming to process and analyze unstructured data. Email is an example of unstructured data. Structured and unstructured are two important types of big data.
Semi-structured
is the third type of big data. Semi-structured data pertains to the data containing both the formats mentioned above, that is, structured and unstructured data. To be precise, it refers to the data that although has not been classified under a particular repository (database), yet contains vital information or tags that segregate individual elements within the data. Thus we come to the end of types of data. Let’s discuss the characteristics of the data.
How Big Data Works
Big data gives you new insights that open up new opportunities and business models. Getting started involves three key actions:
1. Integrate
Big data brings together data from many disparate sources and applications. Traditional data integration mechanisms, such as ETL (extract, transform, and load) generally aren’t up to the task. It requires new strategies and technologies to analyze big data sets at terabytes, or even petabytes, scale.
During integration, you need to bring in the data, process it, and make sure it’s formatted and available in a form that your business analysts can get started with.
2. Manage
Big data requires storage. Your storage solution can be in the cloud, on-premises, or both. You can store your data in any form you want and bring your desired processing requirements and necessary process engines to those data sets on an on-demand basis.
Many people choose their storage solution according to where their data is currently residing. The cloud is gradually gaining popularity because it supports your current compute requirements and enables you to spin up resources as needed.
3. Analyze
Your investment in big data pays off when you analyze and act on your data. Get new clarity with a visual analysis of your varied data sets. Explore the data further to make new discoveries. Share your findings with others. Build data models with machine learning and artificial intelligence. Put your data to work.
Check it out Latest Jobs In Big Data: Click here
If You Want To Get More Daily Such Tech Updates, Career Advice Then Join the Telegram Group From Given Link And Never Miss Update.
Join Telegram Group of Daily Jobs Updates for 2010-2021 Batch: Click Here
TCS NQT 2021 Registration Begins, Check Hiring Process, Eligibility Criteria, and Test Pattern: Click here
Why You’re Not Getting Response From Recruiter?: Click here
Top 5 High Salary Jobs in India IT Sector 2020: Click here
How To Get a Job Easily: Professional Advice For Job Seekers: Click here
Cognizant Latest News: Up To 20K+ Employees Will Be Hired: Click here
Jio vs Airtel vs Vodafone- Idea 2 Gb Per Day Data Plan Comparison: Click here
Lenovo Legion Three Gaming Laptops Launched In India: Click here
COVID-19 Live Tracker India & Coronavirus Live Update: Click here
Career Tips for Freshers: Top 7 Hacks To Land Your Target Job: Click here
Feel Like Demotivated? Check Out our Motivation For You: Click here
List of Best Sites To Watch Free Movies Online in 2020: Click here










































